All RFID systems need antennas to transmit and receive signals. But not all antennas are created equal. There are a variety of factors you need to consider when choosing the right UHF RFID antenna for your application. This blog post will help you navigate the options and make the best decision for your needs. So, read on to learn more!
What is a UHF RFID Antenna?
Radiofrequency identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that is used widely to identify and track objects and transfer data by attached tags automatically. The Antenna emits and receives waves as a signal.
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID Antenna works in a frequency range band.
Introduction to UHF RFID Antenna:
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for the Radio frequencies that ranges between 300 Megahertz (MHz) to 3 Gigahertz (GHz). The corresponding wavelengths to these frequencies are 10 centimeters to 1 meter.
Electromagnetic waves are generated as a signal from an antenna used to read and extract the information stored in an RFID chip of tags. Antennas generate different electromagnetic wave fields and travel different distances.
Importance of UHF RFID Antenna:
The UHF RFID Antenna system is a modern technology that is helpful in numerous ways. It saves cost and time, provides more efficient results with the advantages of several applications in diverse fields.
1- Resourceful option
UHF RFID antennas are more resourceful than standard barcode technology because they read multiple tags stored in just one chip.
2- Diversified applications
UHF RFID antennas are used for various applications like tracking systems, inventory or product location identification, and laundry management purposes.
3- Automatic and Authentic
UHF RFID antennas provide real-time automated and authentic data, which saves time and energy,
4- Instant and bears a heavy load of data
A UHF RFID system is an instant and real-time data collection system for heavy loads of information.
5- Cost-effective technology
A UHF RFID technology is more cost-effective than in the past.
How Does UHF RFID System Works?
The UHF RFID system is really simple to understand. It mainly consists of 03 parts, a fixed RFID reader, A UHF RFID Antenna, and a passive RFID tag.
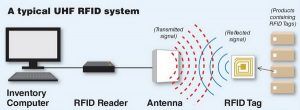
The reader receives and sends the RF Signal To/From the Antenna. After that, it decodes the signals received. Then it interprets the data present in that tag in the form of digital information.
The antenna function is to catch the radio waves which are being generated by the tag and further send it to the reader for decoding purposes.
The tag chip serves the function of memory storage. It stores Productselectronic product code (EPC) and other capricious information. The purpose of keeping this information is that it can be read and tracked by an RFID reader whenever is required.
Applications of UHF RFID Antenna:
UHF RFID systems are used for numerous tenacities. Applications of these systems range from tracking a product to supply chain management. Potential applications of these systems are
- Assets management
- Access Control
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Laundry and Textile Industries
- Product/Vehicle tracking
- Race time tracking
- Inventory/Files tracking
- Logistics and materials companies
- Warehousing
- Library management
These applications are expanding and becoming endless.
Types of UHF RFID:
There are three main types of UHF RFID technologies based on their electromagnetic spectrum. This spectrum is divided into three frequency ranges.
1- Low-Frequency :
- The frequency range is between 30 to 300 kHz, primarily 125-134 kHz
- Read range is zero to 10 centimeters
- This range works best for near liquids and metals.
- As this falls in a very short range of frequency, so it has a low data transmission rate and high production cost.
2- High-Frequency :
- The frequency range is 13.56 MHz
- Read range is zero to 30 centimeters
- This range has large memory options to store and meets global standards but has a low transmission rate.
3- Ultra-High Frequency :
- The frequency range is 300 to 3000 MHz (433 MHz, 860-960 MHz)
- Read range is zero to 30 centimeters
These are further divided into 02 types of RFID such as
1. Active RFID
The frequency range is 433 MHz (2.45 GHz can be used under very high-frequency range)
Read range is from 30 to 100+ meters
This has a very long read range, large memory capacity, and high transmission rates.
This has a high interface with metals and liquids, some restrictions on shipment, requires complex software, and costs high per tag.
2. Passive RFID
The frequency range is 860 to 960 MHz.
Read range is zero to 25 meters depending on the input power and antenna gain.
This has a very long read range, costs low per tag, and meets global standards and high transmission rates.
It has high equipment cost, a high interface with metals and liquids, and a moderate capacity to store memory.
What are the Ranges of UHF RFID Antennas?
There is a vast range of UHF RFID antennas that are made to cater to the requirements. So, it provides different options for selection according to various requests. After analyzing the requirements, one can choose the best suitable model for the application.
So, these antennas can be selected according to the frequency range and the read range.
Frequency Range of UHF RFID Antennas:
The primary frequency ranges of UHF RFID include 433MHz, 865-868MHz, 902-928MHz, and 860-960MHz.
The frequency bands of UHF RFID slightly differ for different countries and areas in the world due to regional regulations. That’s why the frequency bands for UHF RFID are different for the US, Europe, and other regions in the world.
Most of the UHF RFID antennas are specified between 860 to 960MHz. Two mainly used and common operation frequency ranges are FCC (federal communication commission) which operates at 902-928 MHz, and ETSI European telecommunication standards institute) which operates at 865-868MHz. Most of the countries and regions in the world follow either FCC or ETSI.
At Sanny Telecom, we offer FCC(902-928MHz) Series RFID Antennas, ETSI(865-868MHz) Series RFID Antennas, and global 860-960mhz series RFID antennas to customers all over the world. The performance has been optimized to match each band in different areas.
Read Range of UHF RFID Antennas:
It is very difficult to measure the accurate read range of the Antenna, specifically with a passive UHF RFID system. Significantly it depends upon some factors such as
- Sensitivity of RFID IC (Integrated circuit)
- RF power output level of the reader
- The gain of the Antenna
The higher the power, the more sensitivity of IC, and the higher the gain of the Antenna, the farther the range of RFID and vice versa.
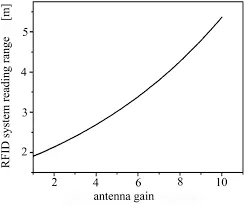
There are some factors that impact the read range of antennas, such as cable length and environmental factors. Some interference tests should be done to make the UHF RFID system a good match to minimize these effects.
At SANNY TELECOM, we offer a wide range of UHF RFID antennas. The read range ranges from 16 feet(5m) to 99 feet (30m) or higher based on the normal output power ≤1 watt (30dbm). Typically, the read range of 8dbi circular polarization is about 12m and 25m for a 12dbi linear polarity RFID antenna. Furthermore, the read range of the linear Antenna is a little farther than a circular antenna based on the same gain and size. The below table shows the details based on different frequency ranges, gain, polarization,
| Frequency | Polarization | Gain | Read Range | Reader |
| 865-868MHz | Circular | 5.5dBi | 7m | / |
| 902-928MHz | Circular | 5.5dBi | 5m | / |
| 865-868MHz | Circular | 8dBi | 15m | Impinj |
| 865-868MHz | Linear | 8dBi | 17m | Impinj |
| 902-928MHz | Circular | 8dBi | 13m | Impinj |
| 902-928MHz | Linear | 8dBi | 15m | Impinj |
| 865-868MHz | Circular | 9dBi | 19m | Impinj |
| 902-928MHz | Circular | 9dBi | 17m | Impinj |
| 865-868MHz | Circular | 12dBi | 25m | / |
| 865-868MHz | Linear | 12dBi | 27m | / |
| 902-928MHz | Circular | 12dBi | 20m | / |
| 902-928MHz | Linear | 12dBi | 22m | / |
How to choose the UHF RFID Antennas?
There are many options to choose the antennas. You will find the best options for your antennas at SANNY TELCOM.
Gain of UHF RFID Antenna:
The gain of the antennas defines the ratio of the power generated by the Antenna to radiate more or less in any direction. It has something significant to do with the shape, material, and size of the radiation element.
The higher the antenna gain, the longer is the range with narrower beam-width or vice versa. The gain of the Antenna mainly depends on the size of the Antenna. The bigger is the size of the Antenna, the higher is the gain of the Antenna or vice versa.
At Sanny Telecom, there are three common series of UHF RFID antennas. One is a low gain (5/6dbi) series; another is a middle gain (8/9dbi) series and the last high gain (11/12dbi) series. However, some specific custom antennas can reach as high as 15dbi with ultra-narrow beam-width. Select the suitable antenna gain based on the shape of your interrogation zone and coverage needs.
Polarization of UHF RFID Antenna:
There are two main polarization forms: linear polarization and circular polarization. Further, Linear polarization has two directions, either horizontal or vertical. Two types of circular polarization are right-hand circular polarized (RHCP), which follows a clockwise pattern, and left-hand circular polarization (LHCP), which follows a counterclockwise pattern.
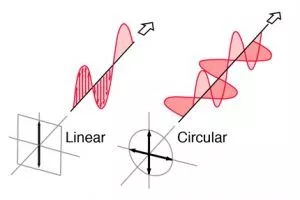
Circular polarization is less affected than linear polarization by “Faraday effects,” which deals with the interaction between light and magnetic field. It is more resistant to signal degradation and much easier to install as well. That’s why RHCP is frequently used for a wide range of applications and is more reliable than other types.
Connector/Port type of UHF RFID Antenna:
It depends upon the interface of the UHF reader. There are three families of connectors:
- N-series (N-female and N-male)

- SMA series (SMA male, SMA female, RP SMA -female, RP SMA-male)

- TNC series (TNC female, TNC male, RP TNC plug, RP TNC jag)

Mounting Type for UHF RFID Antenna:
To choose the best mounting type depending upon the specific applications. Mainly it is based on the environment for the application.
- Indoor: Threaded Studs, mounting holes or wall mount with wall mounting kits
- Outdoor: Normally, a mast/pole mount with a mounting bracket is available. It can be fixed with some pole/mast outdoor.
The Mounting Bracket Type for Outdoor UHF RFID Antenna:
There is a wide range of mounting brackets available at SANNY TELECOM, which are used to mast/pole mount listed below:

- Light duty: It includes one L bracket, two U bolts, and clamps with 30 stainless steel screws and washers. It is only adjustable in up and down motion. It is mostly used for low and middle-gain antennas.

- Heavy-duty style: It consists of four parts (all die-casting aluminum). This robust design is suitable for industrial applications. It is used for higher gain antennas with big sizes such as 12dBi, or 15dBi gain.

- Universal mounting bracket: It is suitable for most of the antennas and mounting options. It is very easy to mount with UDLR (Up, down, left, right), adjustable clamps, and tilts. It has no limits towards the mounting mast/pole diameter and ranges from 38mm to 100mm or bigger with optional 304 stainless steel clamps.

Sometimes, there is no need for mounting brackets when antennas are embedded in an enclosed box.
The Ruggedness of UHF RFID Antenna:
The operation of the antennas mainly depends on the materials and IP rating, which varies in a different environment for outdoor applications. Find some examples below:
When installed on the rails, Antenna Radom must be rugged enough to absorb the impact of high-speed rocks. In extremely hot or cold weather conditions, fiberglass is mostly used to save costs. The IP rating must be IP65 for the Antenna, at least in rainy areas. The maximum wind velocity and service life must be taken into consideration in coastal circumstances.

At SANNY TELECOM, there is a wide range of UHF RFID antennas with different designs, materials, and IP ratings that can be suitable for different environments and all-weather operations. The normal Radom materials range from fiberglass, UV-ABS to PC as well as ASA. The IP rating includes IP54, IP55, IP65, and IP67 for both indoor and outdoor. As a matter of fact, they can be customized in specific applications for all-weather operations.
How to connect the UHF RFID Antenna to the reader?
Two communal ways are primarily used to connect the Antenna to the reader.
- This one has a fixation on the backplate with flanged connectors, which can be mounted on the plate. A pigtail(coax cable assembly ) will be needed to connect the antennas to the reader. Pigtail includes two connectors and a certain length of cable. Mostly, a low loss cable of LMR series such as LMR195, LMR240, or LMR400 is recommended.

- This one has a certain length of a coaxial cable and comes out of either the backplate or the side of the Antenna. No extra cable is required in this case because the length of the coaxial cable can be customized. The recommended cable models are the RG series, XD-FB series, and SYV series.
How To Install The UHF RFID Panel Antenna With Normal Mast Mount Brackets?
The installation process can be easily understood by these 05 steps described below:
Step 1: Fasten the l-bracket with the four screws (supplied) on the backplate of the UHF RFID antenna.
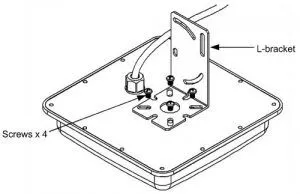
Step 2: Secure the Antenna on a mast or a pole using a fixed clamp and U-bolt. Place a spring lock washer and flat washer on each end of the U-bolt.
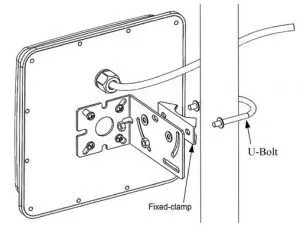
Step 3: Adjust the angle of the U-bolt on the l-bracket and secure the hexagon screw nuts. Make sure it points towards the UHF RFID system that is to communicate with.
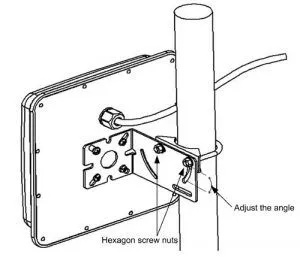
Step 4: Use an M6 wrench or suitable adjustable wrench to tighten the assembly to the mast. Tighten the hex nuts evenly. Do not overtighten.
Step 5: Overview of the mast mount UHF RFID panel antenna.
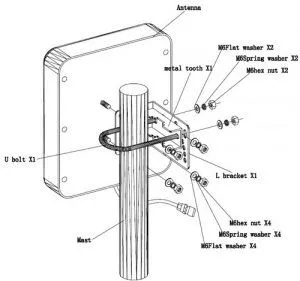
Notes: Make sure the Antenna is positioned so that the arrow labeled v-pol is pointing up. The uncovered drain holes will be on at the bottom of the Antenna Radom, and the covered drain holes will be on the side.
Secure the UHF RFID panel antenna on a mast, column, or pedestal at a height between 1.8 – 2.2 m (5.9 – 7.2 ft) above the ground. Be sure to leave some space to adjust the Antenna’s angle to the upper, lower, left, or right position.
FAQs:
What is the purpose of an antenna in a UHF RFID system?
The Antenna emits and receives electromagnetic waves as a signal. It sends power, data, and commands to the tags.
What is the UHF RFID Protocol in the world?
The international standards organization (ISO) and EPCglobal are two families that approve and control the protocols worldwide. EPC global created a standard format for the EPC (electronic product code), which includes a header, unique EPC identifier, and a filter value.
What is the difference between the active RFID antenna and passive RFID Antenna?
The active RFID antennas have a high-frequency range (433MHz) and a long-read range (30 to 100+meters), so these have high transmission rates.
While the passive RFID antennas have a low-frequency range (860 to 960MHz) and a short read range (contact to 25 meters). So it has high equipment cost and moderate capacity to store memory.
What is the best-fit UHF RFID antenna?
It depends on a lot of factors. The most important one is the impedance matching between the reader and the Antenna. Also, some important parameters need to be taken into consideration such as the gain, polarization, connector type, mounting, and ruggedness. We suggest taking samples for testing purposes first.
How can I boost my UHF RFID antenna signal to extend the read range?
The read range can be increased by following the below guidelines:
1. By increasing the gain with a bigger size of the Antenna
2. By increasing the input power of the reader
3. By reducing the system signal loss
4. Position the antenna with the correct height and direction
What does a UHF RFID antenna look like?
Omnidirectional: This radiates equal power in all directions perpendicular to an axis. These are less powerful as compared to the directional antennas.

Directional: This radiates and receives the power in specific directions, and in this way, interference is reduced. These are more powerful than Omnidirectional and have 03 common types:




