Linear polarization and circular polarization are two different methods of radio frequency (RF) signal transmission and reception. Each has its own advantages and is suited to different applications. Understanding the differences between the two can help you make an informed decision about which type of polarization is best for your specific RFID system requirements.
What is Linear Polarization?
Linear polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field vector in an electromagnetic wave. In a linearly polarized wave, the electric field oscillates in a single plane, while the magnetic field oscillates perpendicular to it. The direction of polarization is determined by the direction of the electric field vector. Linear polarization can be achieved by passing unpolarized light through a polarizing filter or by using certain types of antennas.

Advantages of Linear Polarization
1. Longer read range: Linear polarization typically provides a longer read range compared to circular polarization. This is because the energy of the RF signal is concentrated in a single direction, allowing for greater distance between the reader and the tag.
2. Better penetration: Linear polarization is better at penetrating certain materials, such as liquids and metals. This makes it suitable for applications where tags may be placed on or near these materials.
3. Lower cost: Linear polarization antennas are generally less expensive to manufacture compared to circular polarization antennas.
Application Scenarios for Linear Polarization
1. Long-range applications: Linear polarization is ideal for applications where longer read ranges are required, such as in large warehouses or outdoor environments.
2. Applications with metal or liquid interference: Linear polarization can better penetrate metal or liquid interference, making it suitable for applications in which tags are attached to or near these materials.
3. Cost-sensitive applications: If cost is a major concern, linear polarization may be the better choice due to the lower cost of linear polarization antennas.
What is Circular Polarization?
Circular polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves, such as light, where the direction of the electric field vector rotates in a circular pattern as the wave propagates. In circularly polarized light, the electric field vector traces out a helix or spiral shape in space. This is in contrast to linear polarization, where the electric field oscillates in a straight line, and elliptical polarization, where the electric field traces out an ellipse. Circular polarization can be either right-handed or left-handed, depending on the direction of rotation of the electric field vector.

Advantages of Circular Polarization
1. Better tag orientation: Circular polarization is less affected by the orientation of the tag. This means that tags can be read from any angle, making it easier to achieve consistent and reliable reads.
2. Multiple tag reading: Circular polarization allows for the simultaneous reading of multiple tags, even if they are in different orientations. This makes it ideal for applications where multiple tags need to be read quickly and efficiently.
3. Improved performance in multi-path environments: Circular polarization is less affected by multi-path interference, where signals bounce off objects and create interference. This makes it suitable for applications in environments with many reflective surfaces.
Application Scenarios for Circular Polarization
1. Applications with multiple tags: Circular polarization is ideal for applications where multiple tags need to be read simultaneously, such as in retail inventory management or race timing systems.
2. Applications with varying tag orientations: Circular polarization is suitable for applications where tags can be in different orientations, such as when attached to moving objects or when tags are randomly placed.
3. Applications with multi-path interference: Circular polarization is better suited for environments with many reflective surfaces, such as warehouses with metal shelving or indoor environments with lots of walls and objects.

Why is circular polarization better than linear polarization for the RFID antenna?
Circular polarization is better than linear polarization for RFID antennas for several reasons:
1. Reduced cross-polarization interference: Circular polarization allows the RFID antenna to receive signals from any polarization orientation. This means that even if the RFID tag is oriented at a different angle, the circularly polarized antenna can still receive the signal effectively. In contrast, linearly polarized antennas require the RFID tag to be oriented in the same direction for maximum signal strength. Circular polarization reduces the chances of signal loss due to mismatched polarization between the antenna and the tag.
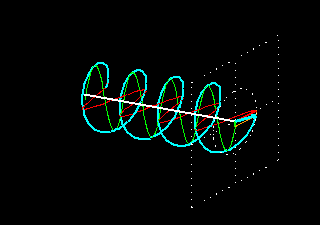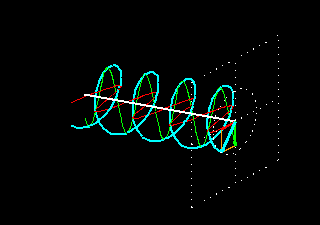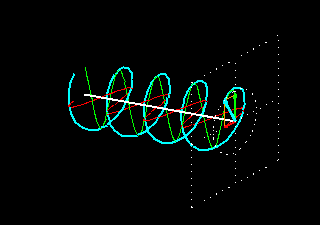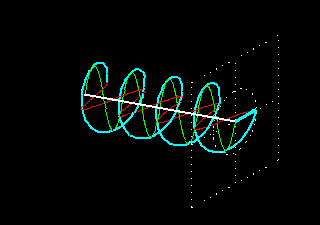
2. No need for directional awareness: With linear polarization, the orientation of the RFID tag is critical for successful scanning. If the tag is not aligned with the linearly polarized antenna, the signal strength decreases significantly. This requires users to be aware of the orientation of the RFID tag during scanning, which can be challenging in real-world scenarios. Circular polarization eliminates the need for directional awareness as it can receive signals from any orientation, providing more flexibility and ease of use.
3. Better performance in multi-path environments: Circular polarization is less affected by multi-path interference, which occurs when the RFID signal reflects off nearby objects and creates multiple signal paths. Linear polarization antennas are more susceptible to multi-path interference because the reflected signals may have different polarization orientations. Circular polarization helps mitigate this issue by receiving signals from all polarization angles, reducing the impact of multi-path interference.
4. Improved read range and coverage: Circular polarization provides a larger read range compared to linear polarization. The ability to receive signals from any polarization orientation allows the antenna to capture more energy from the RFID tag, resulting in a stronger and more reliable signal. This improves the read range and coverage area of the RFID system, allowing for faster and more accurate scanning of tags.
Overall, circular polarization offers significant advantages over linear polarization for RFID antennas, including reduced cross-pol interference, the elimination of directional awareness, better performance in multipath environments, and improved read range and coverage. These benefits make circular polarization a preferred choice for RFID applications.
Summary
In summary, a linear polarization RFID antenna offers longer read ranges, better penetration of certain materials, and lower cost. It is suitable for long-range applications, applications with metal or liquid interference, and cost-sensitive applications.
On the other hand, a circular polarization RFID antenna offers better tag orientation, the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously, and improved performance in multipath environments. It is suitable for applications with multiple tags, varying tag orientations, and environments with multi-path interference.
By considering the advantages and application scenarios of each, you can make an informed decision about which type of polarization is best for your RFID system requirements.


